
| Bibliographic Entry | Result (w/surrounding text) | Standardized Result | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faugh, Jerry S. & Serway Raymond A. College Physics. Pacific Grove: CA: Thomson Brooks/Cole, 2003. | Average Earth-Moon distance: 3.84 × 108 m | 768,000 km | ||||||||||||
| The World Book Encyclopedia. Chicago: World Book Inc., 2005: 783. |
| 768,934 km | ||||||||||||
| North, Gerald. Observing the Moon. United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 2005: 2. | 'It orbits the Earth at a mean distance of 384,000 km' | 768,000 km | ||||||||||||
| Sagan, Carl. Murmurs of Earth. New York: Random House, 1978: 226. |
| 768,800 km | ||||||||||||
| Jones, Brain. The Practical Astronomer. New York: Simon and Schuster Inc, 1990: 16. | 'However, the distance between the Earth and Moon varies from 356,410 km (222,756 miles) at perigee, or closest approach to 406,697 km (254,186 miles) at aposee, its farthest point'. | 712,820 km to 813,394 km | ||||||||||||
How Does The Moon Orbit The Earth
The moon is really just a large piece of rock, which was caught in the Earth's gravitational field. Because the moon has a smaller mass than the Earth, 7.35 × 1022 kg compared to 5.98 × 1024 kg, the moon orbits around the Earth, making the moon Earth's satellite. In fact, the moon is the Earth 's one and only natural satellite.
So how was the diameter of the moon's orbit determined? One possible way would be finding the Earth-Moon distance. To find the Earth-Moon distance, scientists could use a RADAR laser, in which they can fire electromagnetic waves or em waves at the moon and time how long it takes for the em waves to travel to the moon and back. Since em waves always travel at the speed of light (3 × 108 m/s), and the time can be measured, one can use the equation v = s/t or s = vt, but don't forget to divide the measured time or the calculated distance by 2, as the em waves traveled twice the distance. The moon's distance from the Earth varies from 360,000 km to 406,000 km, making the mean distance from the Earth 384,000 km. Since its mean distance from the Earth is 384,000 km, the average length of the moon's orbit's diameter is 768,000 km.
Is the moon really moving farther away from the Earth? Yes, it is. The moon is moving about 3.8 cm farther away from the Earth every year. This occurs because of tidal interactions. The moon's gravitational force pulls on the Earth making it bulge ar the face of the Earth the moon is facing. These are called 'tidal bulges'. The tidal bulges would affect the force of gravity on the moon, as the bulge would have a greater gravitational pull on the moon than the center of the Earth. And since the Earth rotates faster than the moon orbits, the tidal bulges would move ahead of the moon and pull the moon towards the tidal bulge causing the moon to speed up and move ahead in its orbit. Note: The moon is only moved very little by this in a day, so don't get crazy.
Collin Tam -- 2005
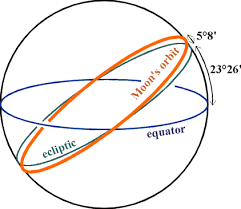
A moon on an inclined (tilted) orbit, passing above and below the equator of the planet, will have its tidal bulge constantly moving up and down. The movement of the bulge leads to friction and heat. The Moon’s elliptical orbit. The Moon varies in size because the Moon’s orbit around Earth is egg-shaped, so at one point it’s closest and at another it’s furthest away. The Moon orbits the Earth, and the Earth orbits the Sun, and the Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way, which orbits within the Local Group, which is a part of the Virgo Supercluster.

What is a Moon?
Moons – also known as natural satellites – orbit planets and asteroids in our solar system. Earth has one moon, and there are more than 200 moons in our solar system. Most of the major planets – all except Mercury and Venus – have moons. Pluto and some other dwarf planets, as well as many asteroids, also have small moons. Saturn and Jupiter have the most moons, with dozens orbiting each of the two giant planets.
Moons come in many shapes, sizes, and types. A few have atmospheres and even hidden oceans beneath their surfaces. Most planetary moons probably formed from the discs of gas and dust circulating around planets in the early solar system, though some are 'captured' objects that formed elsewhere and fell into orbit around larger worlds.
Moons Orbit Planets
Explore in 3D—Eyes on the Solar System
Lunar Orbit
Eyes on the Solar System lets you explore the planets, their moons, asteroids, comets and the spacecraft exploring them from 1950 to 2050. Ride with the Curiosity Rover as it lands on Mars or fly by Pluto with the New Horizons spacecraft all from the comfort of your home computer.
Moons Orbit Saturn
Eyes on the Solar System ›